Understanding Anxiety Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that involve excessive worry, fear, or nervousness. While it is normal to experience occasional anxiety in response to stressful situations, anxiety disorders are characterized by persistent and intense feelings of unease that can interfere with daily life. These disorders affect millions of people worldwide, and understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for promoting mental well-being.
Types of Anxiety Disorders:
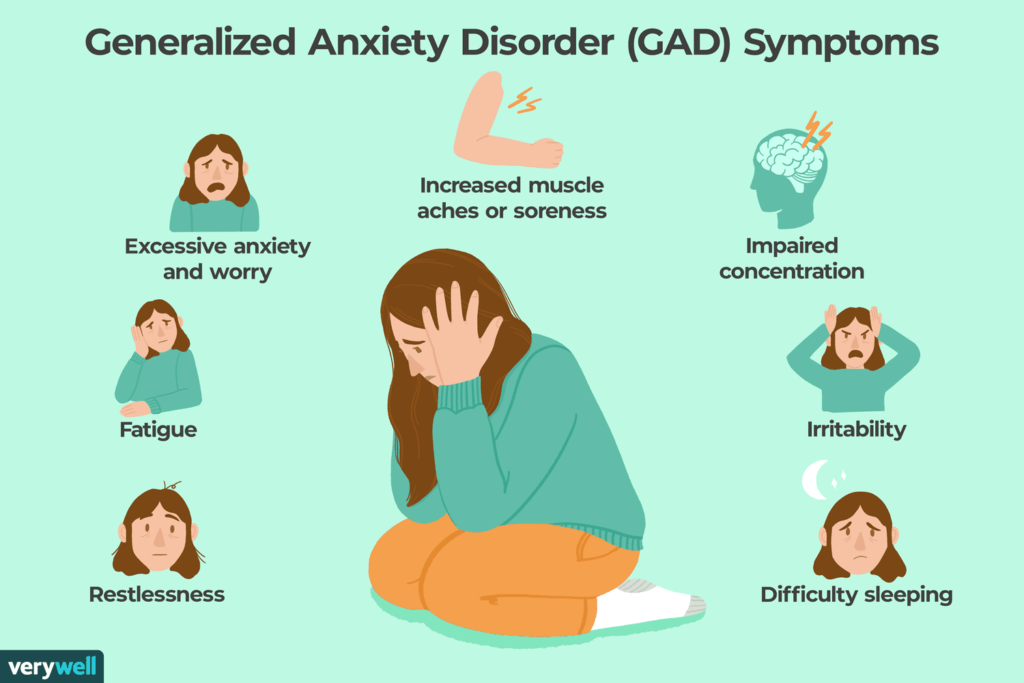
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Individuals with GAD experience chronic and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, relationships, and health. This worry is often disproportionate to the actual situation.
- Panic Disorder: Panic disorder involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms like a racing heart, sweating, and shortness of breath.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: People with social anxiety disorder fear social situations and the judgment of others. This fear can lead to avoidance of social interactions, impacting both personal and professional aspects of life.
- Specific Phobias: Specific phobias are intense and irrational fears of particular objects or situations, such as heights, flying, or animals. Avoidance behaviors are common among individuals with specific phobias.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): OCD is characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) performed to alleviate anxiety. Common obsessions include fears of contamination or harm.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): PTSD can develop after exposure to a traumatic event. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety related to the traumatic experience.
Causes of Anxiety Disorders:
The exact causes of anxiety disorders are complex and often involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Some common contributing factors include:
- Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders may increase the risk of developing similar conditions.
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers, can contribute to anxiety disorders.
- Personality and Temperament: Individuals with certain personality traits, such as being more prone to negative thinking or excessive worrying, may be more susceptible to anxiety disorders.
- Trauma and Stress: Exposure to traumatic events or chronic stress can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders:
The symptoms of anxiety disorders can vary depending on the specific type of disorder, but common manifestations include:
- Excessive Worry: Persistent and uncontrollable worry about everyday situations.
- Physical Symptoms: Increased heart rate, muscle tension, sweating, trembling, and fatigue.
- Avoidance: Avoidance of situations or activities that trigger anxiety.
- Irrational Fears: Intense fears of specific objects or situations.
- Panic Attacks: Sudden and overwhelming episodes of fear and physical symptoms.
- Obsessions and Compulsions: Intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors performed to alleviate anxiety.
Treatment Options:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is an effective approach for many anxiety disorders. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Medications: Antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and beta-blockers are among the medications used to manage anxiety symptoms. However, these should be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can contribute to overall mental well-being.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help manage stress and anxiety.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide valuable support and understanding.
In Conclusion:
Anxiety disorders are common but treatable conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Seeking professional help is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and the development of an effective treatment plan. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anxiety disorders, individuals and their loved ones can work towards managing and overcoming these challenging conditions, promoting mental health and well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, reaching out to a mental health professional is an important first step towards recovery.