Understanding Muscle Spasms: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Muscle spasms, often referred to as muscle cramps, are involuntary contractions of one or more muscles. While they are generally harmless, they can be uncomfortable and, in some cases, even painful. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for muscle spasms is crucial for managing and preventing these involuntary muscle contractions.
Causes of Muscle Spasms:
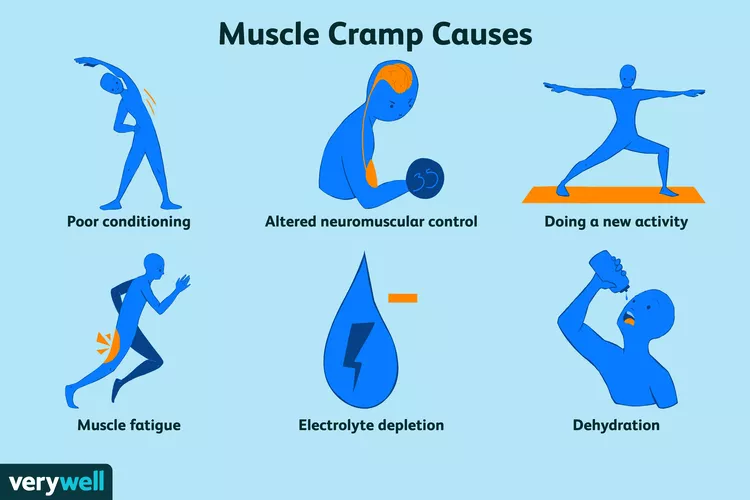
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to dehydration, causing an imbalance of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium. This imbalance can trigger muscle spasms.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Disruptions in the normal levels of electrolytes in the body, particularly potassium, calcium, and sodium, can contribute to muscle spasms.
- Overexertion: Intense physical activity or overexertion, especially when the body is not adequately conditioned, can result in muscle fatigue and spasms.
- Poor Blood Circulation: Inadequate blood flow to the muscles can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients, triggering spasms.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, statins, and medications for high blood pressure, may contribute to muscle spasms as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions, including nerve compression, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can increase the likelihood of experiencing muscle spasms.
Symptoms of Muscle Spasms:
- Sudden Pain: Muscle spasms are often characterized by a sudden, sharp pain in the affected muscle.
- Involuntary Muscle Contractions: The primary symptom is the involuntary contraction of muscles, which can range from mild twitches to severe cramps.
- Temporary Muscle Stiffness: After the spasm subsides, individuals may experience temporary muscle stiffness in the affected area.
- Visible Twitching: In some cases, muscle spasms may be visible as twitching or a bulging of the muscle.
Treatment and Prevention:
- Hydration: Ensuring proper hydration is crucial in preventing muscle spasms. Adequate fluid intake helps maintain electrolyte balance in the body.
- Stretching Exercises: Regular stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle spasms. Focus on stretching the muscles prone to cramping.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium can help prevent electrolyte imbalances that may trigger muscle spasms.
- Warm-Up and Cool Down: Before engaging in strenuous physical activity, it’s essential to warm up the muscles. Cooling down after exercise can also prevent muscle fatigue.
- Massage and Heat Therapy: Massaging the affected muscle and applying heat can help relax tight muscles and alleviate spasms.
- Medication Adjustments: If muscle spasms are a side effect of medication, consulting with a healthcare professional to adjust the dosage or explore alternative medications may be necessary.
In Conclusion:
While muscle spasms can be inconvenient and painful, they are often preventable and manageable through lifestyle adjustments and proper care. Understanding the underlying causes and adopting a proactive approach to muscle health can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of muscle spasms, promoting overall well-being and physical comfort. If muscle spasms persist or become chronic, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.